

If it’s an unknown address, the switch blocks the respective port and stops the communication attempt. Once a connection has been established from one segment to another, the intermediate coupling element checks the MAC address of the sender device and matches it with an administrator-created whitelist. Switches can separate big networks into smaller segments. At the network level, linking elements such as Ethernet switches via port security provide the opportunity to filter network data traffic on the OSI layer 2. To protect IT systems from internal and external dangers, administrators sometimes implement security measures that restrict access to the LAN to authorized devices. Basically, spoofing is a resolution strategy for troubleshooting – but in most cases, it’s used for the infiltration of foreign systems and illegal network activities instead. Other than MAC addresses, other popular targets for spoofing attacks are the internet protocol (IP), domain name system (DNS), and address resolution via Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). Hackers use this method of attack to conceal their own identity and imitate another.
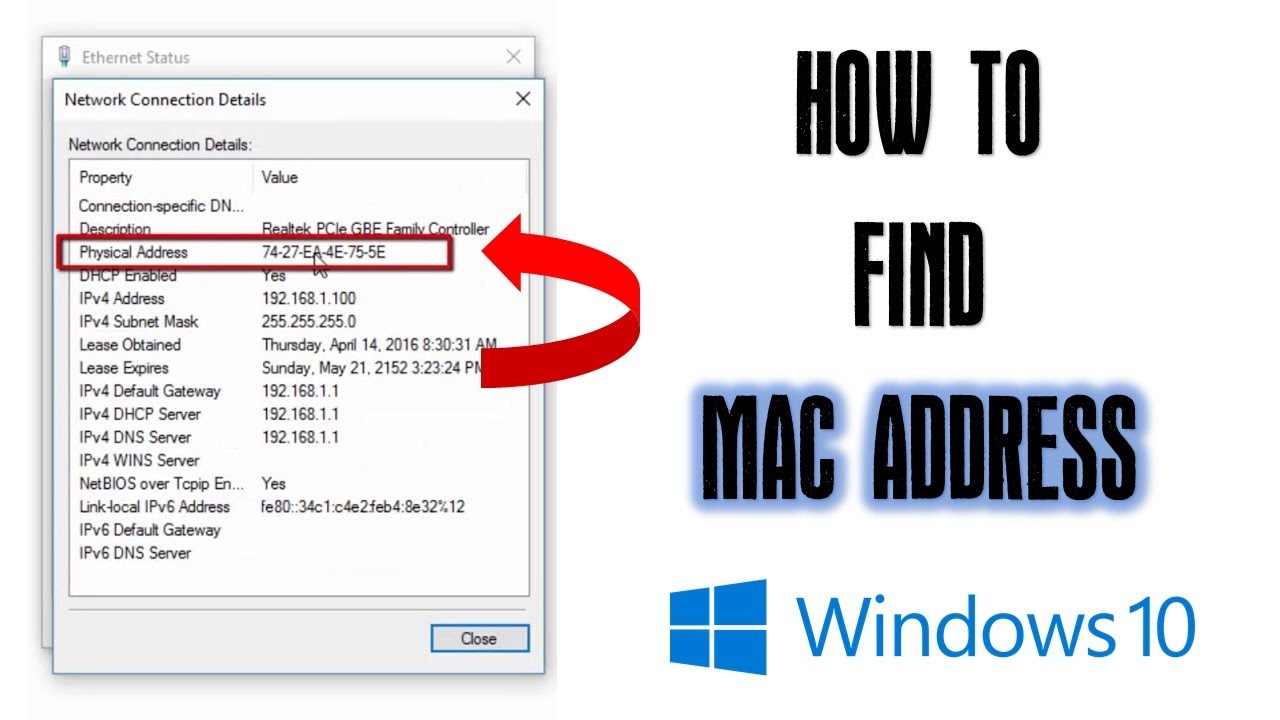

Every MAC address includes 48 bits, or 6 bytes, and is arranged in the following pattern: 00:81:41:fe:ad:7e. MAC addresses: distinct hardware addresses identify network interface controllers (NIC) such as LAN cards or WLAN adapters, and are used to identify devices in local networks.This masking is what’s referred to as MAC spoofing. But it is possible to mask it on the software side. Users are not able to change or rewrite the MAC address. This burned-in address (BIA) is virtually etched to the hardware by the manufacturer. Every device that’s connected to a network possesses a worldwide, unique, and physical identification number: the Media Access Control address, or MAC for short.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
